Eclim provides wastewater treatment systems for hospitals hotline 0941.113.286
The number of patients and number of hospital beds is increasing due to population growth or some hospitals and medical facilities increasing their capacity to meet medical examination and treatment needs, leading to the amount of wastewater and garbage at some places. The number of hospitals increased. Therefore, the hospital's wastewater treatment system needs to be installed, repaired and upgraded to suit the scale of development, health care needs of the people and ensure technical regulations and standards. environmental country.
Outstanding advantages:
The wastewater treatment system helps quickly reduce the concentration of pollution in wastewater before being discharged into the outside environment. As the latest, most advanced technology...the system possesses many outstanding advantages compared to conventional treatment systems:
Hospital wastewater is wastewater generated from hospitals and wastewater contains harmful toxins such as pharmaceutical residues, disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and harmful chemicals.
Untreated hospital wastewater contains many sources of pathogens, chemical and physical substances that are harmful to human health and the environment. Therefore, treating hospital wastewater before discharging it into the environment is necessary and needs to be prioritized during the process of hospital construction and development.
Sources of hospital wastewater generation
Hospital wastewater includes two sources: medical wastewater and domestic wastewater.
The characteristics of these types of wastewater are that they contain many impurities, chemicals (such as formaldehyde, mixed chemicals, etc.), organic substances, nutrients, and detergents (such as salts of acids). higher fats) and especially bacteria, viruses, parasites (such as salmonalla, shigella, gastrointestinal viruses, etc.), various biological pathogens in blood, pus,… and even including toxic radioactive substances
Parameter values and pollutants are specified in QCVN 28: 2010/BTNMT National Technical Regulation on Medical Wastewater
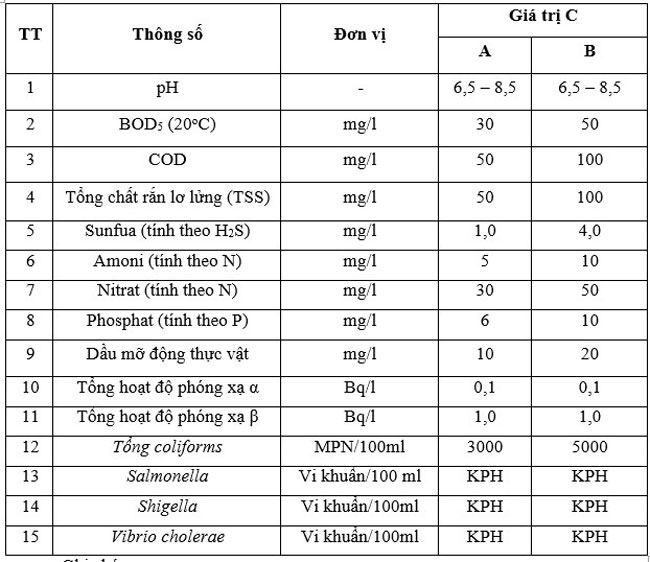
Note:
In Table 1:
Column A specifies the C values of parameters and pollutants as a basis for calculating the maximum allowable value in medical wastewater when discharged into water sources used for domestic water supply purposes.
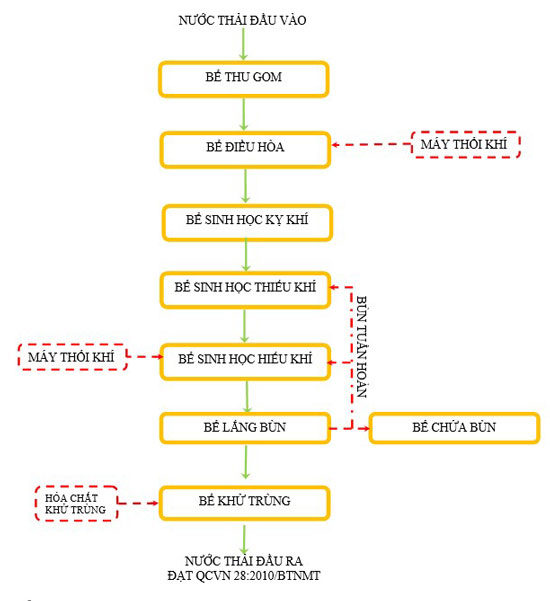
1. Collection tank:
The collection tank is responsible for concentrating hospital wastewater. Before the water reaches the collection tank, it passes through a mesh to remove coarse trash and large substances in the wastewater. Then water from the Collection Tank is pumped to the Equalization Tank.
2. Air conditioning tank:
3. Anaerobic biological tank:
Wastewater after being conditioned and stabilizing the flow will be pumped to the anaerobic tank. Here, thanks to the decomposition of organic substances in an anaerobic environment, anaerobic microbial strains grow, develop, and convert pollutants in wastewater into nutrients for cells, reducing pollution concentration in wastewater.
After anaerobic treatment, wastewater is directed to the downstream treatment facility.
4. Anoxic biological tank:
- Domestic wastewater contains a large amount of nutrients Nitrogen and Phosphorus, these are two nutrients that cause eutrophication of receiving sources and negatively affect the water environment, so they need to be treated. removed before discharging into receiving sources.
- In the Anoxic anoxic biological tank, under anoxic conditions, anoxic microorganisms develop and process N and P through the process of Nitrification and Phosphoril.
5. Aerobic biological tank:
The main function of the aerobic biological tank is to convert ammonium in wastewater into Nitrite and Nitrate. Part of the amount of nitrate produced during the aerobic process will be circulated back to the anoxic tank to carry out the denitrification process, part will be retained in the activated sludge and settled in the biological sedimentation tank. The nitrification and denitrification process will reduce the concentration of ammonium and nitrate in wastewater, so the treated wastewater meets connection standards. The nitrification process is expressed by the equation below:

The process of reducing organic substances such as BOD and COD is carried out along with the process of removing N and P nutrients.
6. Biological sedimentation tank
- Biological sedimentation tank is a tank that separates biological sludge from clean water after treatment.
- The mixture of sludge and wastewater leaves the aerobic biological tank and overflows into the biological sedimentation tank to conduct the water and sludge separation process. The sludge flocs will settle to the bottom of the settling tank and will be circulated by the sludge pump to the Aerotank to maintain the activated sludge concentration when necessary. If there is excess sludge in the tank, the sludge will be pumped and discharged into the sludge tank.
- The clear water is concentrated on the surface of the settling tank, collected by a surface water collection pipe system, the water flows into the disinfection tank itself.
- The excess sludge is pumped and discharged into the sludge tank, the sludge separation water is circulated back to the equalization tank and the wastewater treatment process continues. The excess sludge after separating a portion of the water will be collected and processed by the sludge collection unit.
7. Sludge Storage Tank: A tank that receives excess sludge
8. Disinfection Tank
The clear water after settling is collected and led to the disinfection tank. At the disinfection tank, disinfectant chemicals (chlorine or ozone) are used to disinfect and kill coliforms in wastewater before being discharged into the receiving source.
Treated wastewater meets discharge standards according to QCVN 28:2010/BTNMT, Column B.

0 comments