Pollution of urban water environment
Currently, water pollution is a worrying problem in Vietnam, although agencies and industries have tried to implement many policies and laws on environmental protection. Industry and urbanization are growing at a rapid pace, putting the region's water resources under pressure.
Wastewater, exhaust gases and solid waste are polluting the water environment in many cities, industrial parks and craft villages. Hundreds of industrial production facilities in big cities are polluting water due to lack of waste treatment facilities and equipment.
Industrial production causes a lot of water pollution. For example, in the textile, paper, and pulp industries, wastewater typically has an average pH of 9 to 11; Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and biochemical oxygen demand (COD) index can be up to 700mg/l and 2,500mg/l; Suspended solids content can be up to 25% and higher than the allowable limit. The wastewater content of these companies contains cyanide (CN-) exceeding 84 times the standard, H2S content exceeding 4.2 times and NH3 content exceeding 84 times the standard. Therefore, surface water sources in residential areas have been seriously polluted.
Industrial parks, export processing zones and concentrated industrial clusters have high levels of water pollution. Industrial wastewater from paper, washing powder, dyeing and textile factories totaling 500,000 m3/day pollutes the water source in Tham Luong industrial cluster, Ho Chi Minh City.
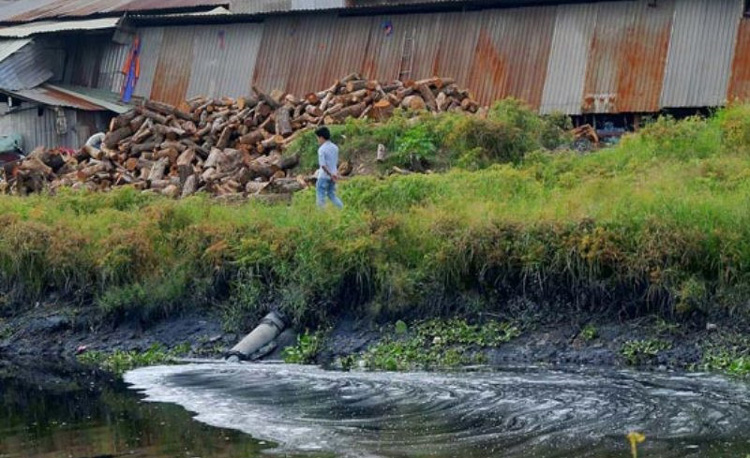

Untreated wastewater is discharged directly into Tham Luong canal (illustration)
Industrial wastewater in Thai Nguyen city comes from paper manufacturing facilities, iron and steel smelting, non-ferrous metallurgy and coal mining. Wastewater from paper production has a pH of 8.4-9, has an NH4 content of 4mg/1, has a brown color and an unpleasant odor.
In some craft villages in Bac Ninh that produce iron, steel, copper casting, aluminum, lead, paper and textile dyeing, thousands of m3/day of untreated wastewater pollute the environment and water sources.
Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City are the cities with the highest levels of water pollution. Domestic wastewater in these cities is directly discharged into receiving sources, such as rivers, lakes, canals or ditches, without a centralized treatment system. In addition, many manufacturing facilities do not treat wastewater, most hospitals and large medical facilities do not have wastewater treatment systems, and a lot of solid waste is not collected. is one of the main sources of water pollution.
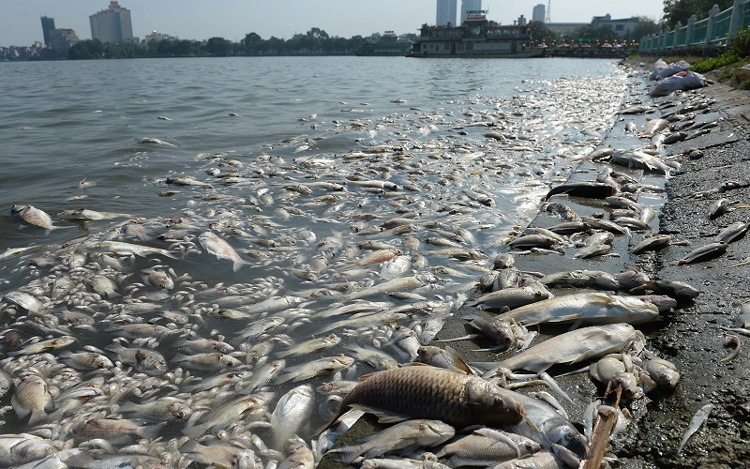

Fish carcasses surfaced at the edge of West Lake.
Currently, canals, rivers and lakes in big cities are seriously polluted. Hanoi city has a total wastewater volume of 300,000–400,000 m3/day, with 36/400 new production facilities and hospitals having wastewater treatment systems. Currently, only 5/31 hospitals have wastewater treatment systems, accounting for 25% of hospitals' wastewater. In addition, the BOD index, dissolved oxygen, NH4, NO2, NO3 in rivers, lakes, and ditches in the inner city all exceed allowed regulations.
The total amount of waste in Ho Chi Minh City amounts to nearly 4,000 tons per day, but only 24/142 large medical facilities in the city are capable of treating wastewater and about 3,000 polluting production facilities in the city. area must be relocated.
Not only in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh, but also in Hai Phong, Hue, Da Nang, Nam Dinh and Hai Duong. The pollution of domestic wastewater is also not treated. The parameters of suspended matter (SS), BOD, COD and dissolved oxygen (DO) all exceed the allowable standards (TCCP), even exceeding 20 times the TCCP.
Water pollution in rural areas
Currently, nearly 76% of Vietnam's population lives in rural areas, where infrastructure is backward and most untreated human and livestock waste seeps into the ground or is washed away, causing increased organic and microbial pollution in water sources.
According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the average number of Feca coliform bacteria is 1,500–3,500 MNP/mL in areas along the Tien and Hau rivers, and in irrigation canals is 3800–12,500 MNP/mL. Due to agricultural production, water sources such as rivers, lakes, canals and ditches are polluted, endangering the water environment and people's health.
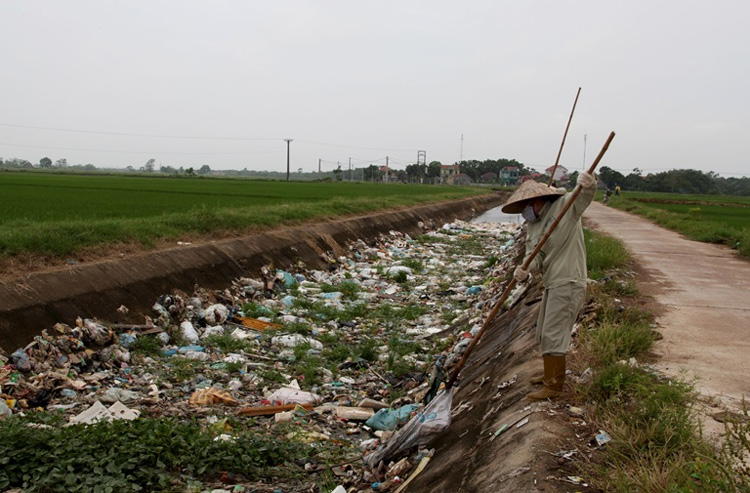

The drainage canal system is filled with garbage.
By 2001, the whole country had 751,999 hectares of water surface used for aquaculture, according to statistics from the Ministry of Fisheries. Massive aquaculture, without planning and without following technical procedures, has caused many negative consequences for the water environment.
During the aquaculture process, along with improper use of chemicals, residual food settles to the bottom of ponds, lakes and river beds. This pollutes the water environment with organic matter, causing the growth of a number of disease-causing organisms.
Factors causing water pollution
Water pollution can be caused by many objective and subjective factors, such as population growth, modernization, industrialization, backwardness and weak infrastructure. However, people's awareness of environmental issues is still not high.
Environmental management and protection activities are not really good. Water pollution is a type of pollution that is dangerous every day and difficult to overcome for human life and the sustainable development of the country, but the awareness of many levels of government, management agencies, and organizations is Organizations and individuals responsible for protecting the water environment are inadequate.
There are very few regulations on water environment management and protection. For example, there are no technical regulations and procedures for water resource management and protection.

Illustration.
The mechanism for assignment and coordination between agencies, sectors and localities is overlapping and unclear in terms of responsibilities. There are no plans to exploit, use and protect water resources for large basins and territories. There are no reasonable regulations related to financial contributions to water environment management and protection, leading to lack of finance and insufficient revenue to spend on the water environment. The investment budget for water environmental protection is still very low. Although some countries in ASEAN have invested 1% of GDP in this field, Vietnam has only reached 0.1%.
There are too few community education programs about the environment and water. Water environment managers are insufficient in number and of poor quality. In Vietnam, there are on average 3 environmental managers for every million people, while in some ASEAN countries there are 70 environmental managers for every million people.